CTEPH-Detect is a single-center, randomized controlled trial of an EPIC Best Practice Advisory (BPA) alert-based decision support tool. CTEPH-Detect is set to enroll 400 patients seen in the outpatient setting at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. The first aim of the study is to determine the impact of a BPA, using EPIC on echocardiographic screening for CTEPH in patients with prior pulmonary embolism (PE) and symptoms/signs suggestive of pulmonary hypertension or recent pulmonary testing suggesting unexplained respiratory symptoms. The second aim of the study was to determine the impact of an EPIC BPA on the diagnosis of CTEPH in patients with prior PE and symptoms/signs suggestive of pulmonary hypertension or recent pulmonary testing suggesting unexplained respiratory symptoms.
Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Outcome in a Study of the Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Anticoagulation Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit.
Code Aorta is a single-center, retrospective, prospective analysis, and quality improvement study. The study analyzes the data of patients admitted to Brigham and Women’s Hospital with acute aortic syndrome (AAS). The study is set to enroll 1,000 patients either admitted to inpatient service with an AAS or outpatients identified as having a history of an AAS. The primary objective of the study is to determine if improvements in coordination of care and systematic follow up in patients with AAS improve outcomes. The secondary objectives of this study are to determine the natural history of subtypes of AAS and to characterize risk markers that may be useful for prognosis or informing therapeutic decision-making including imaging characteristics, available blood tests, and clinical characteristics.
The Discharge eAlert study is a randomized controlled trial which investigates the impact of a computerized decision support strategy on patients at high risk of venous thromboembolisms (VTE). Discharge eAlert aims to increase the frequency of VTE prophylaxis in high-risk patients. The study aims to determine whether alerting physicians about the importance of VTE prophylaxis prior to the time of planned hospital discharge will lower the incidence of outpatient VTE. The two strategies implemented were devising a risk score that reliably and quickly identified patients of high-risk of VTE and randomizing high-risk patients without prophylaxis into an intervention group or control group.
AF-ALERT was a U.S.-based, single-center, randomized controlled trial investigating electronic alert-based computerized decision support (CDS) to increase prescription of anticoagulation in high-risk AF patients in the inpatient setting who are not prescribed anticoagulation. One goal of the study was to enroll 2000 eligible subjects to determine the impact of electronic alert-based on prescription of anticoagulants in high-risk patients in the outpatient setting. The other goal was to determine the impact of electronic alert-based computerized decision support on the frequency of stroke and systemic embolic events in high-risk patients in the outpatient who are not prescribed anticoagulation.
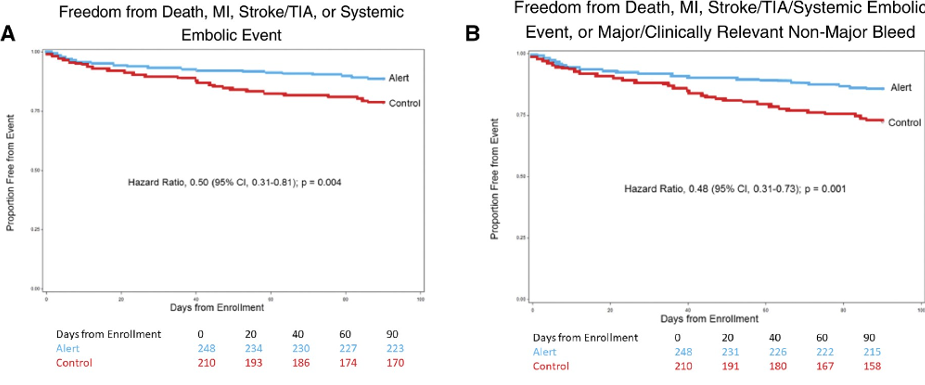
Kaplan–Meier curves for freedom from death, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident (stroke or transient ischaemic attack), and systemic embolic event at 90 days (A), Kaplan–Meier curves for freedom from major adverse events at 90 days (death, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, systemic embolic event, and major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding) (B), cumulative incidence of myocardial infarction at 90 days.
AF-ALERT2 was a randomized controlled trial to evaluate an alert-based computerized decision support (CDS) program to identify ambulatory care clinic patients with AF and increased stroke who do not have an active prescription for anticoagulation. The goal of the study was to determine the impact of alert based CDS on prescription of anticoagulation for high-risk ambulatory clinic patients not already prescribed anticoagulation.

The AF-ALERT3 Trial is a multicenter randomized controlled trial investigating the impact of electronic alert-based computerized decision support (CDS) on outpatients with atrial fibrillation. The first aim of the study is to determine the impact of alert-based CDS that includes stroke and bleeding risk assessments on prescription of anticoagulation at 90 days in high-risk ambulatory AF patients in the community medical center setting who are not being prescribed anticoagulation at the time of the clinical encounter. The second aim of the study is to determine the impact of alert-based CDS that includes both stroke and bleeding risk assessments on failure to prescribe anticoagulation due to perceived risk of bleeding in high-risk ambulatory AF patients in the community medical center setting who are not being prescribed anticoagulation at the time of the clinical encounter. Lastly, the third aim is to determine the impact of alert-based CDS that includes stroke and bleeding risk assessments on the frequency of stroke, TIA, and systemic embolic events at 6 months in high-risk ambulatory AF patients in the community medical center setting who are not being prescribed anticoagulation at the time of the clinical encounter.
This is a 600-patient U.S.-based, single-center, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily for extended prevention of recurrence after provoked VTE in adult patients with at least one persistent provoking factor who have completed at least 3 months of standard therapeutic anticoagulation. The patient randomization is 1:1 to either apixaban 2.5mg orally twice daily for 12 months or oral placebo twice daily for 12 months. The design of the HI-PRO trial have been published in Thrombosis and Haemostasis and follow up is expected to be completed by December 2024.
The HI-PRO Cohort Study is a one-year follow-up of patients with provoked VTE and at least one enduring factor who have previously completed the HI-PRO randomized controlled trial of extended-duration low-dose apixaban to prevent recurrence. The single-center cohort study is designed to include the 600 patients formally enrolled in the HI-PRO trial. The study is set to investigate the natural history of VTE risk and understand the management of VTE recurrence in the 12-month period immediately following conclusion of the HI-PRO trial.
PREVENT-HD was a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, pragmatic Phase 3 study investigating the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban to reduce the risk of major venous and arterial thrombotic events, hospitalization, and death in medically ill outpatients with acute, symptomatic COVID-19 infection. The primary objective of the study was to evaluate whether rivaroxaban reduces the risk of a composite endpoint of major venous and arterial thrombotic events, all-cause hospitalization, and all-cause mortality compared with placebo in outpatients with acute, symptomatic COVID-19 infection. The secondary objective was to evaluate whether rivaroxaban reduces the risk of all symptomatic VTE, major arterial thrombotic events and all-cause mortality in outpatients with acute, symptomatic COVID-19 infection.
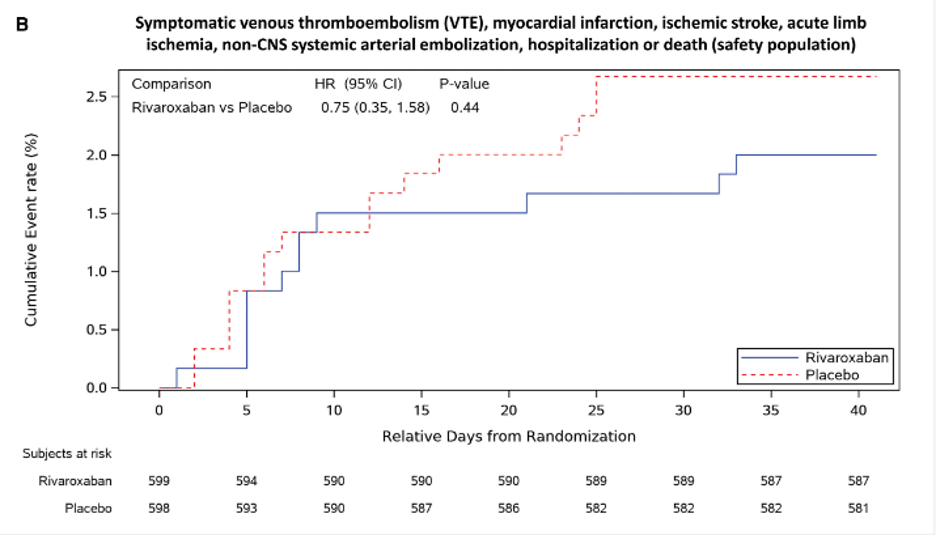
Kaplan-Meier plot of time to the first occurrence of the primary efficacy outcome of symptomatic venous thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute limb ischemia, non–central nervous system systemic arterial embolization, hospitalization, or death in safety (B) populations. Primary efficacy events accrued at a higher rate in the earlier period of follow-up, with almost all the events occurring before 25 days after randomization. Randomization date is considered day 1, and follow-up time is relative to the randomization date. P value (2 sided) for rivaroxaban vs placebo is from the log-rank test, stratified by the time from a positive COVID-19 test to randomization (at 1–5 days and at 6–14 days), with treatment as the only covariate. HR indicates hazard ratio.
CKD-Detect is an alert-based study to detect chronic kidney disease in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. This study is based on the American Diabetes Associations guidelines for all patients with T2DM to undergo an annual measurement of urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR). The goal of this study is to increase guideline-directed assessment of CKD using urine albumin creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have not had a UACR in the past year.
Optalyse-3D is a study evaluating patients who have been treated with anticoagulation alone or mechanical thrombectomy plus anticoagulation, using a novel 3-dimensional reconstruction technique. This cutting-edge approach provides direct information about RV physiology, perfusion of the distal pulmonary arteries, and has the potential to provide more accurate prognostic data than the commonly used surrogate of RV-diameter-to-LV-diameter ratio. As a result, data derived from this technology may offer new perspectives on the effect of anticoagulation alone or mechanical thrombectomy plus anticoagulation in PE patients.
The Sex Differences in Presentation, Risk Factors, Drug and Interventional Therapies, and Outcomes of Elderly Patients with Pulmonary Embolism study (SERIOUS-PE study) seeks to understand how sex is related to PE disease presentation, treatment strategies, and outcomes across multiple countries. This study uses data from US Medicare Fee-For-Service Beneficiaries database and the Registro Informatizado Enfermedad TromboEmbolica (RIETE) registry to view sex differences in PE presentation, risk factors-morbidities, drug and interventional therapies, and 30 day and 1-year outcomes. Findings from this study will address knowledge gaps related to sex differences in older adults with PE using robust pre-specified statistical methods. The study rationale and design has been published previously and findings for the sex differences in clinical presentation were recently published, while other comparisons are still ongoing.
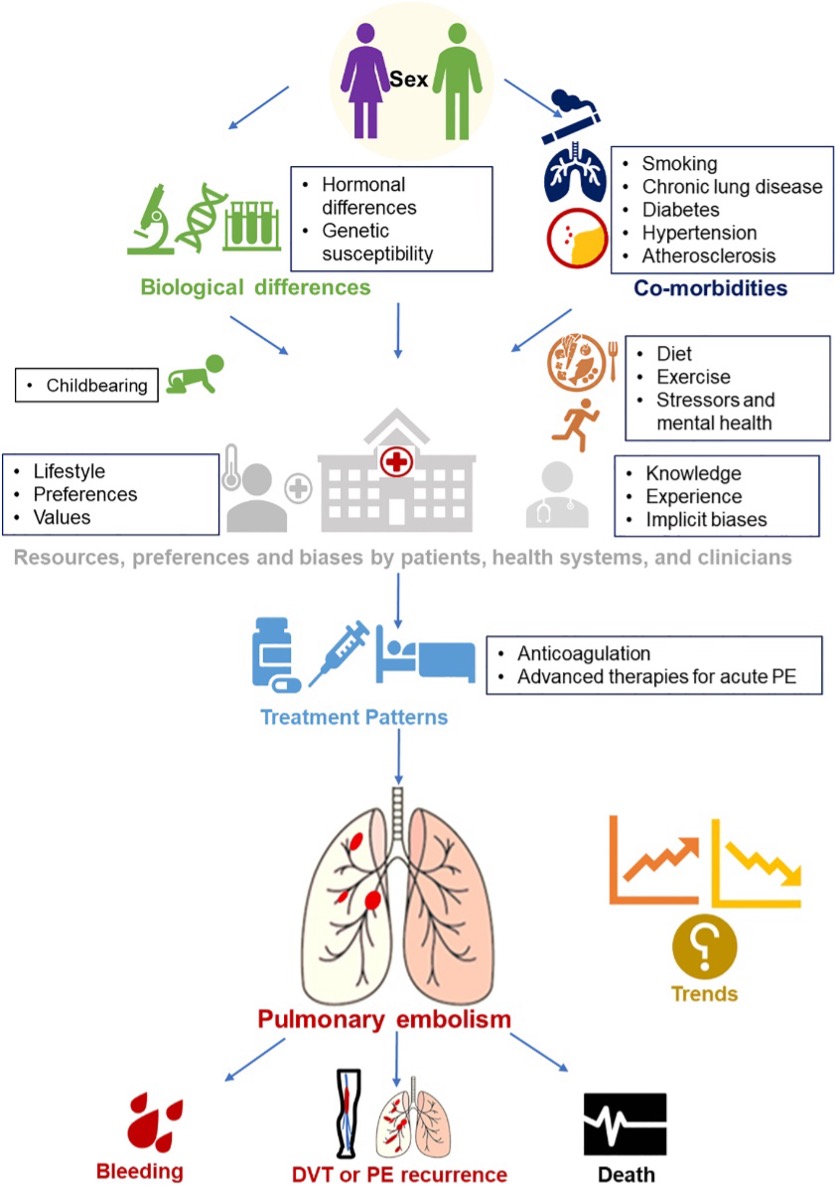
Conceptual model of factors associated with sex differences in PE incidence, treatment and outcomes.
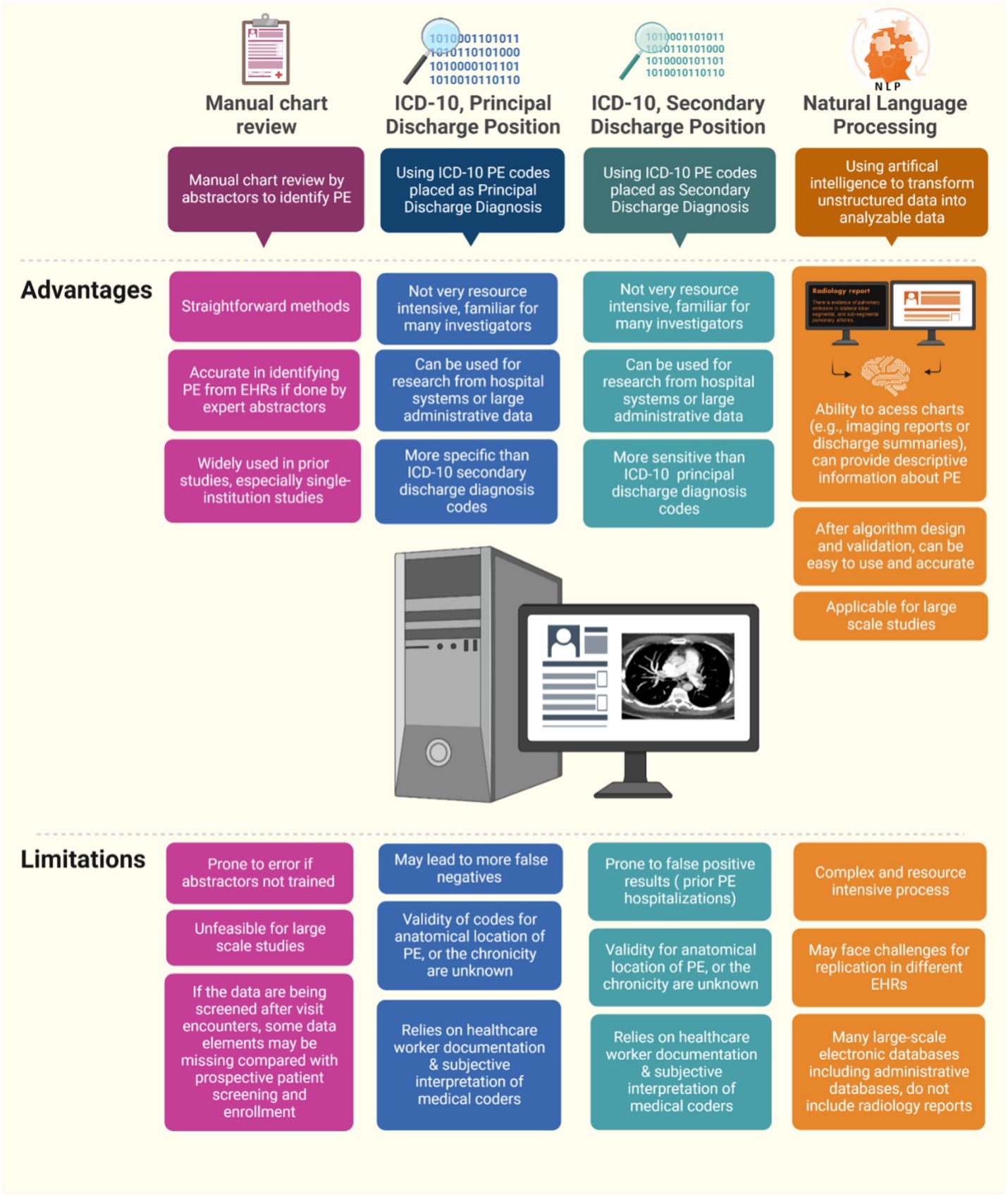
The PE-EHR+ study aims to identify valid tools for efficient identification of PE in electronic databases such as administrative claims data and electronic health records. This American Heart Association (AHA)-funded project assesses the accuracy of International Classification of Diseases-10 codes (ICD-10) when used as the Principal Discharge Diagnosis or Secondary Discharge Diagnoses and accuracy of two existing natural language processing tools for identifying patients with pulmonary embolism (PE) with reference to manual review by two independent physicians who review the medical records using pre-specified criteria. The study uses data from patients from the Mass General Brigham Health System and the Yale-New Haven Health System. The rationale and design of the study have been published and interim results have been presented in several national conferences. Additional analyses are forthcoming.
The LDL-ALERT study is a single-center randomized-controlled trial that has enrolled 400 patients treated for cardiovascular diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. This research study seeks to investigate whether an alert-based computerized decision support strategy can be effective in optimizing lipid management. This clinical research initiative also strives to address the underutilization of lipid-lowering therapies in both inpatients and outpatients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Within the 400 patients enrolled, 200 are in the “inpatient cohort” and 200 are in the “outpatient cohort”; this will help us understand the impact of the computerized decision support strategy in different hospital settings.
The SONIC-PE study is a multicenter, single-arm investigation that will enroll 60 total patients at sites throughout the United States. It seeks to understand whether patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism can be effectively treated with ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed fibrinolysis using the ultrasonic core catheter EKOS+™ system. An initial group of 10 patients will be enrolled; they will receive a total dose of 8 mg tPA given as 2 mg/hour/catheter over 2 hours. This will then be followed by 50 patients who will receive a total dose of 6 mg tPA given as 3 mg/hour/catheter given over 1 hour. Ultimately, this study strives to eliminate the patient’s pulmonary embolism while also reducing the risk of major bleeding that has been traditionally associated with full-dose systemic fibrinolysis.
PAD-ALERT is a study focusing on patients with peripheral artery disease who have not been prescribed a lipid lowering therapy. This study aims to increase guideline-directed utilization of statin and statin-alternative LDL-C lowering therapies in patients with PAD through an alert-based computerized decision support approach.
FREYA is a data registry that enrolled 1,000 patients with recurrent miscarriage without a diagnosable reason, referred to Brigham and Women’s Hospital Center of Infertility and Reproductive surgery for evaluation of recurrent pregnancy loss. This study seeks to determine the prevalence of thrombophilia in these patients and describe the outcomes of those receiving prophylactic low-dose anticoagulation for thrombophilia-associated recurrent pregnancy loss, including bleeding and thrombotic events.
FREYA 2 is a single-center, prospective pilot laboratory study seeking to identify and characterize the role of platelets in peripheral blood disease in patients and the impact of taking medications that modulate platelet function or anticoagulants. The primary objective of the study is to characterize the platelet parameters, content, and function of platelets from patients with various disorders to understand the contribution of platelets to human disease and how this is impacted by anti-coagulant medications. To achieve this objective, blood samples from healthy controls are collected and platelets are isolated to understand the impact and role of platelets in thrombotic disorders and how it is influenced by anticoagulants.
INSPIRATION and INSPIRATION-S Trial was a multi-center, randomized controlled trial with a 2×2 factorial design. The objective of the study was to determine the effect of statin treatment versus placebo on clinical outcomes in patients with covid-19 admitted to the ICU. The study intervention was atorvastatin 20mg orally once daily compared for placebo for 30 days. The study showed that in patients with covid-19 admitted to the ICU, atorvastatin 20mg daily compared with placebo was not associated with a significant reduction in the composite of venous or arterial thrombosis, treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or all-cause mortality.
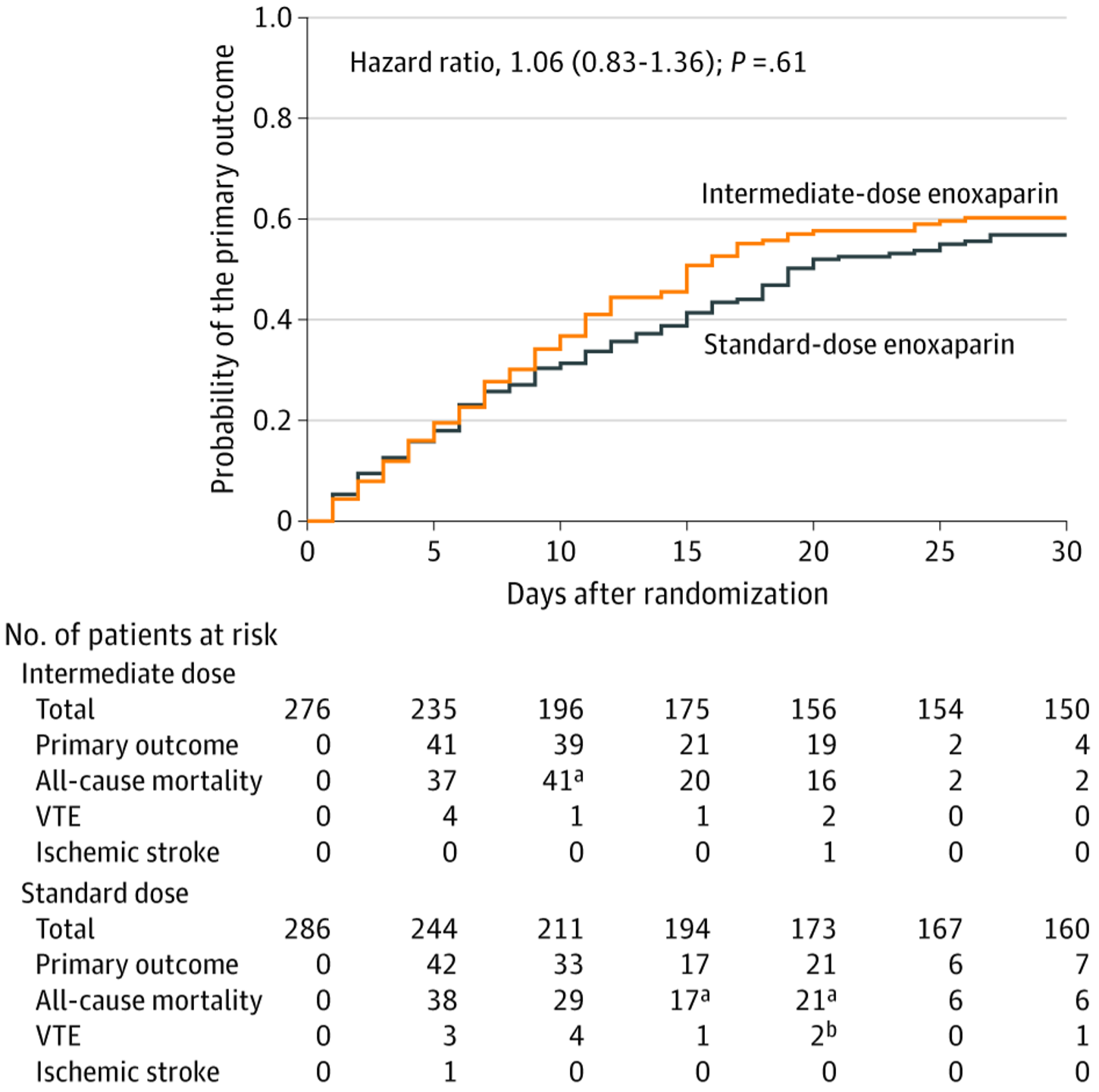
Primary Outcome in the Prespecified Primary Cohort in a Study of the Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit.
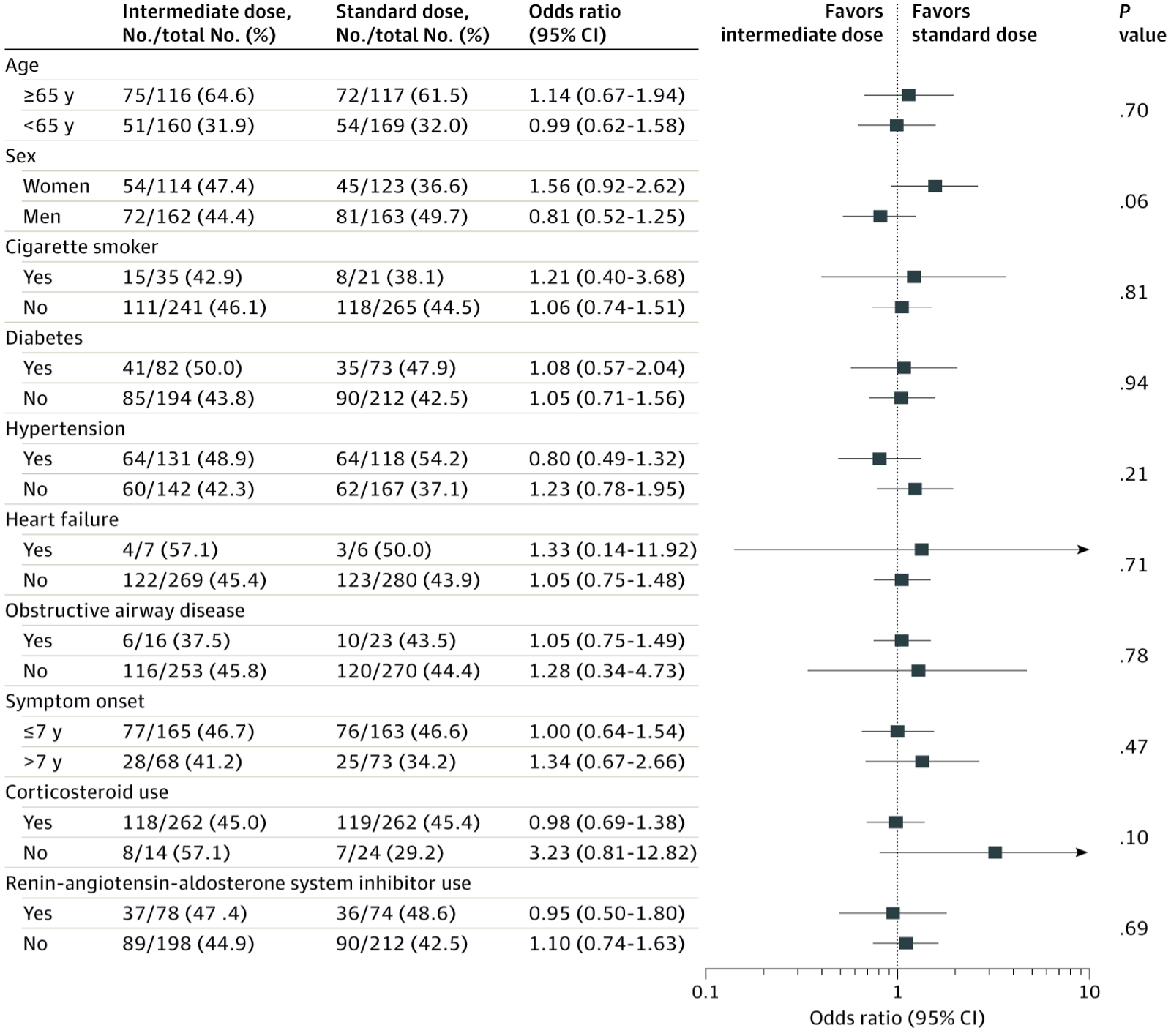
Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Outcome in a Study of the Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Anticoagulation Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit
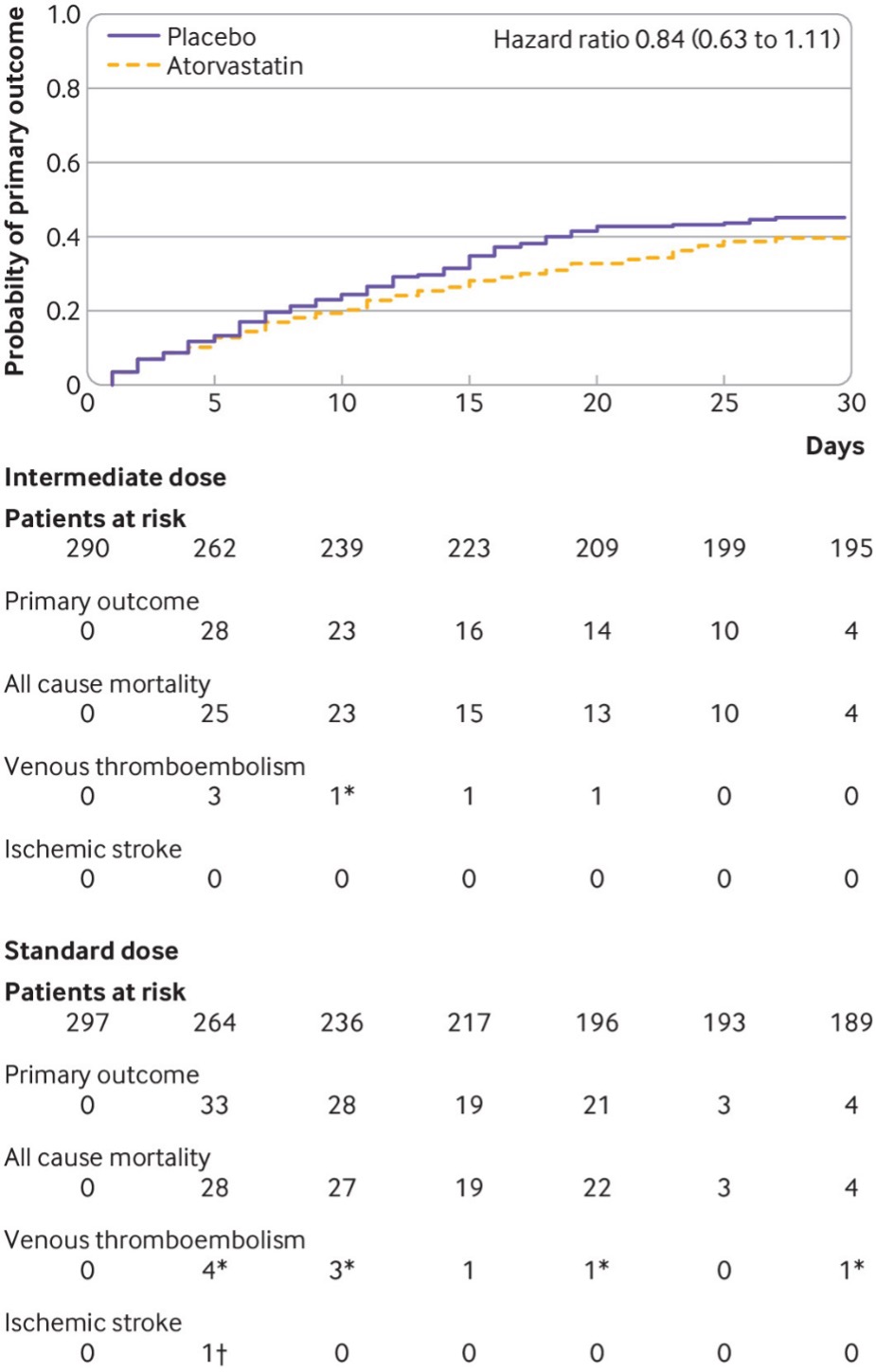
Time to event for the primary outcome, a composite of venous or arterial thrombosis, treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or all-cause mortality during 30 days from randomization, in the prespecified primary cohort, consisting of patients who received at least one dose of the study drug, were not excluded, and did not withdraw consent. *All-cause mortality events were censored by precedent venous thromboembolism events. †Venous thromboembolism event was censored by a precedent ischemic stroke event.
FH-Alert is a single-center, time series trial of a provider-facing EPIC BPA to increase diagnosis, LDL-C lowering, and guideline-based therapy for outpatients with presentations consistent with FH. One of the aims of the study is to determine the impact of provider-facing electronic alert-based CDS on the diagnosis of FH at 6 months from the CDS program. The second focus of the study is to determine the impact of provider-facing EPIC BPA on the mean change in LDL-C levels within 6 months following the triggering of the BPA compared to the most recent LDL-C prior to clinic visit.